The Different Categories in NDIS: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
The National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) is a crucial program designed to support individuals with disabilities in Australia. It provides a wide range of services and assistance tailored to meet the unique needs of participants. To ensure effective delivery of support, the NDIS organizes services into different categories. In this article, we will explore the various categories within the NDIS framework, highlighting their significance and the types of support they offer.
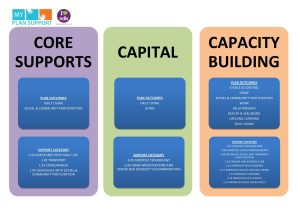
1. Core Supports
Core Supports form the foundation of the NDIS support categories. These supports enable participants to complete daily activities and participate in community life. Under this category, individuals can access assistance with daily personal activities, transportation, consumables, and assistance with community participation. Core Supports aim to enhance independence, promote social inclusion, and enable participants to achieve their goals.
1.1 Daily Personal Activities
Daily Personal Activities support covers assistance with personal hygiene, dressing, eating, mobility, and medication management. It ensures that participants can maintain their personal well-being and carry out essential daily tasks.
1.2 Transport
Transport support assists participants in accessing the community, attending appointments, and engaging in social activities. This category covers costs associated with transport, including vehicle modifications or assistance from a support worker during transportation.
1.3 Consumables
Consumables refer to the products and items that participants need for their daily activities. This may include personal care items, mobility aids, continence products, and other essential supplies. The NDIS provides funding to cover the costs of consumables required by participants.
1.4 Assistance with Community Participation
Assistance with Community Participation enables individuals to engage in social and community activities. It includes support for attending events, joining clubs or groups, and participating in recreational activities. This category aims to enhance social connections, promote inclusion, and foster a sense of belonging.
2. Capital Supports
Capital Supports focus on providing participants with funding for purchasing assistive technology, equipment, home modifications, and capital costs associated with disability support. These supports are divided into two sub-categories:
2.1 Assistive Technology
Assistive Technology refers to devices or systems that assist individuals with disabilities in performing tasks, increasing independence, or improving their quality of life. This category covers aids such as wheelchairs, hearing aids, communication devices, and home modifications to accommodate assistive technology.
2.2 Home Modifications
Home Modifications support participants in modifying their living environment to enhance accessibility, mobility, and independence. This may include installing ramps, handrails, bathroom modifications, and other changes that make the home more accessible and functional for individuals with disabilities.
3. Capacity Building Supports
Capacity Building Supports aim to improve the skills, independence, and opportunities of participants. This category is divided into several sub-categories, each focusing on specific areas of development and support:
3.1 Support Coordination
Support Coordination assists participants in navigating the NDIS system, managing their budgets, and connecting with service providers. Support coordinators work closely with participants to identify and access appropriate services, ensuring their support plans are implemented effectively.

3.2 Improved Living Arrangements
Improved Living Arrangements support helps participants transition to alternative living arrangements, such as shared accommodation or specialist disability accommodation. It also covers support services related to daily living, meal preparation, and household tasks.
3.3 Increased Social and Community Participation
Increased Social and Community Participation focuses on supporting participants in expanding their social networks, participating in community activities, and developing social skills. This can include assistance with joining clubs, attending social events, and accessing community resources.
3.4 Finding and Keeping a Job
Finding and Keeping a Job support aims to enhance participants’ employment prospects and facilitate their successful integration into the workforce. It includes assistance with job searching, resume building, interview skills, workplace modifications, and ongoing support in the workplace.
3.5 Improved Relationships
Improved Relationships support focuses on developing participants’ interpersonal and communication skills, fostering healthy relationships, and addressing specific relationship challenges. This can involve counseling, therapy, social skills training, and support in building and maintaining meaningful connections. https://inclusivementalhealth.org/ndis-provider-victoria/
3.6 Improved Health and Wellbeing
Improved Health and Wellbeing support encompasses a range of services to enhance participants’ physical and mental health. It may include access to allied health professionals, therapy services, exercise programs, and support for managing health conditions.
3.7 Improved Learning
Improved Learning support aims to enhance participants’ educational opportunities and outcomes. It covers services such as tutoring, assistive technology for learning, specialized educational programs, and support for transitioning between educational settings.
3.8 Improved Life Choices
Improved Life Choices support focuses on empowering participants to make informed decisions and exercise choice and control over their lives. It includes capacity building activities, decision-making support, and assistance in managing funding and budgets.
Conclusion
The National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) offers a comprehensive range of support categories to address the diverse needs of individuals with disabilities. Core Supports provide essential assistance for daily activities, transportation, consumables, and community participation. Capital Supports enable participants to acquire assistive technology and make home modifications, while Capacity Building Supports focus on skill development, employment, social participation, relationships, health, education, and life choices.
Understanding these categories is vital for participants and their families to access the appropriate support and maximize the benefits of the NDIS. By aligning support with specific needs and goals, the NDIS aims to enhance the quality of life and promote the inclusion and participation of people with disabilities in Australian society.

